Loading Flow


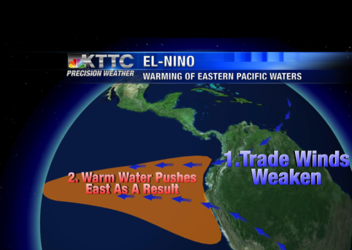
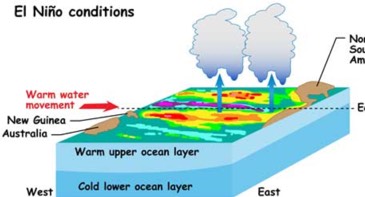
El Niño is the phenomenon when the trade winds slacken, forcing warm Pacific waters to move east, not west, causing extreme weather.
An abundance of hot water in the eastern Pacific causes a lot of evaporation, which then causes excessive rains and floods in South America.
The atmosphere affects the ocean during El Niño by slowing the trade winds, which causes warm water not naturally to move east which in return raises temperature and humidity in the atmosphere.
The failure of cold, nutrient-rich water to upwell causes anchovies to flee Peru which hurts the fishing industry.
El Niño: Disaster For South America
A flood in a Peruvian village caused by El Niño.
A dropsonde is a device dropped in mid-air that measures the speed of the trade winds to help scientists determine if they slow, which would cause an El Niño to help warn places like Peru and Chile.
A floating dropsonde.
A picture of El Niño's effect on South America.
A diagram of the changes during El Niño on the ocean and atmosphere.

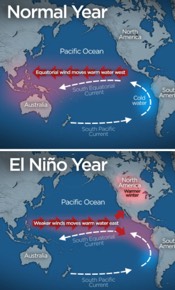
A visual showing the difference between a normal and El Niño year.
Ethan Zucker


