Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

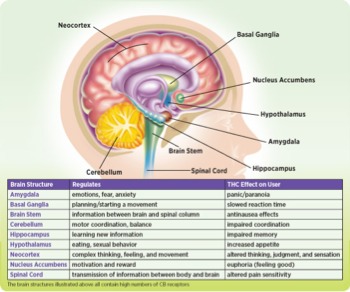
How Does Marijuana Affect the Brain?
When marijuana is smoked, THC rapidly passes from the lungs into the bloodstream, which carries the chemical to the brain and other organs throughout the body. It is absorbed more slowly when ingested in food or drink.
However it is ingested, THC acts upon specific molecular targets on brain cells, called cannabinoid receptors. These receptors are ordinarily activated by chemicals similar to THC called endocannabinoids, such as anandamide. These are naturally occurring in the body and are part of a neural communication network (the endocannabinoid system) that plays an important role in normal brain development and function.
The highest density of cannabinoid receptors is found in parts of the brain that influence pleasure, memory, thinking, concentration, sensory and time perception, and coordinated movement. Marijuana overactivates the endocannabinoid system, causing the high and other effects that users experience. These include distorted perceptions, impaired coordination, difficulty with thinking and problem solving, and disrupted learning and memory.