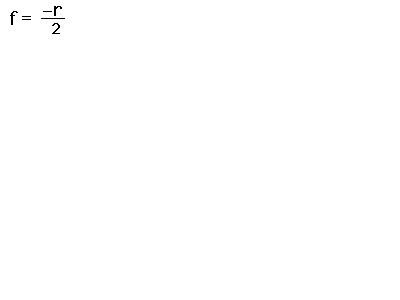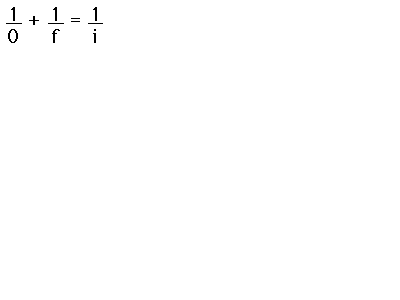Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

Mirror equation
The equation for image formation by rays near the optic axis (paraxial rays) of a mirror has the same form as the thin lens equation:
From the geometry of the spherical mirror, note that the focal length is half the radius of curvature:
As in the case of lenses, the cartesian sign convention is used here, and that is the origin of the negative sign above. The radius r for a concave mirror is a negative quantity (going left from the surface), and this gives a positive focal length, implying convergence.