Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

hollow tubes of tubulin proteins
-> maintain the shape of the cells during mitosis by forming spindle fibers to help separate the chromosomes
-> form a pair of structures known as centrioles, which is located near the nucleus of animal cells to help organize cell division
-> build projections, or cilia and flagella from the cell surface to enable cells to move through liquids
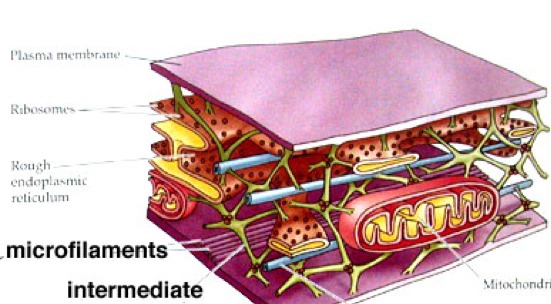
Microtubules
threadlike structure of actin proteins
-> form extensive networks and produce a tough, flexible framework for structural support
-> its assembly and disassembly helps the cytoplasmic movement of cells
Microfilaments