Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

Economics
In the period from 1965-1985 represented a time of tremendous economic growth. This growth was caused by the dramatic rise in oil prices, which were related to the 1973 Arab- Israeli War and the 1979 Iranian revolution. The newfound wealth was a widening in the income gap among the Middle Eastern states, meaning that while all the states increased their national wealth during this period, some states grew at substantially faster rates than others. On the higher end of the gap, major oil-producing states, especially those in the Gulf with small populations, were able to achieve in comes per person rivaling and some cases surpassing, western european economic levels. Jordan and Yemen remained amongst the poorest in the world.
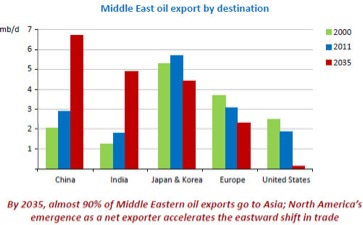
Two factors are currently affecting the economic growth and development in the middle east. The first factor is the high rate of population growth. There is a 3% average population growth per year in the region. Which means that the population in a given state will double about every 20-30 years. The second factor affecting the economic future of the middle east is fluctuations, in either direction - in the price of oil.
Political
There is no single, agreed -upon definition of what specifically constitutes the middle east. Defining the middle east through ethnicity, religion, or national identity is problematic. Therefore, for the purposes of this module, the middle east will include the states of Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, Kuwait, Iran, Syria, Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan and Israel.