Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

Compare the functions of lysosomes and peroxisomes
Lysosomes:
* spherical membranous bags containing digestive enzymes
* digest ingested bacteria, viruses, and toxins
* breakdown glycogen and release thyroid hormone
* breakdown nonuseful tissue
* breakdown bone to release Ca2+
* secretory lysosomes- found in white blood cells, immune cells, and melanocytes
Peroxisomes
* mebranous sacs containing oxidases and catalases
* detoxify harmful or toxic substances
* neutralize dangerous free radicals
* free radicals- highly reactive chemicals with unpaired electrons (i.e., O2-)
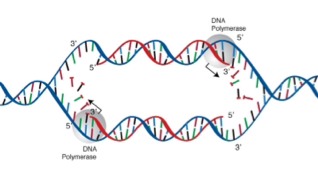
DNA Replication:
The double helix unwinds. The enzyme helicase seperated the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds. After that, the enzyme DNA polymerase pairs each of the two strands with the correct nitrogenous bases. The too stated is the "leading strand" and the bottom strand is the "lagging strand." Then the enzyme lipase glues together the different fragments of the lagging strand of DNA. Now there are 2 replications of DNA each with 46 chromosomes called daughter cells.
