Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

Transition Elements
Transition Elements consist of the following metals:
-Scandium ( Sc )
-Yttrium ( Y )
-Titanium ( Ti )
-Zirconium ( Zr )
-Hafnium ( Hf )
-Rutherforduv ( Rf )
-Vanadium ( V )
-Niobium ( Nb )
-Tantalum ( Ta )
-Dubnium ( Db )
-Chromium ( Cr )
-Molybdenum ( Mo )
-Tungsten ( W )
-Seaborgium ( Sg )
-Manganese ( Mn )
-Technetium ( Te )
-Rhenium ( Re )
-Bohrium ( Bh )
-Iron ( Fe )
-Ruthenium ( Ru )
-Osmium ( Os )
-Hassium ( Hs )
-Cobalt ( Co )
-Rhodium ( Rh )
-Iridium ( Ir )
-Meitnerium ( Mt )
-Nickel ( Ni )
-Palladium ( Pd )
-Platinum ( Pt )
-Unununium ( Uuu )
-Zinc ( Zn )
-Cadmium ( Cd )
-Mercury ( Hg )
-Ununbium ( Uub )
Transition Metals are in fact:
-Luster
-Malleable
-Ductile
-Conductive
-Reactive
Mercury is liquid at room temperature and poisonous

Example of a Transition Metal -->
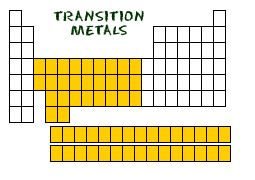
Transition Metals are located in groups 3-12
Iron is a strong metal that is used in manufacturing machine tools, automobiles, hulls of large ships, machine parts, and even building parts.
Nickel is used for desalination
Copper is used to make wires
Gold is used for fashion and jewerly to please the eye.
Zinc is used in plastics, inks, soaps, batteries, and electrical equipment
Cadmium is used in some control rods and shields within nuclear reactors