Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

Cholecystokinin: Its Contribution to Control of Digestive Enzyme Secretion by the Pancreas
- indicated by the presence of food in the upper small intestine
- a polypeptide containing 33 amino acids
- passes by way of the blood to the pancreas which secretes more pancreatic digestive
enzymes (70 - 80% after a meal)
- results especially from the presence of proteoses and peptones and long-chain fatty acids
in the chyme from the stomach
Cholecystokinin
1. intense sodium bicarbonate secretion in response to acid in the duodenum, stimulated by secretin
2. a dual effect in response to soap (a fat)
3. intense digestive enzyme secretion (when peptones enter the duodenum) stimulated by cholecystokinin
Release of Cholecystokinin
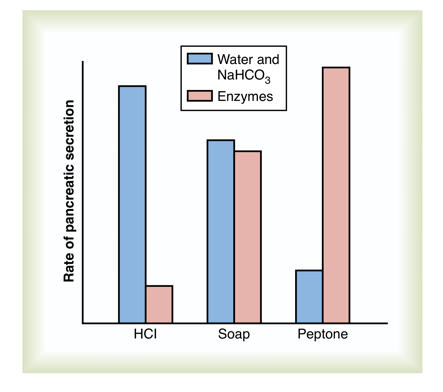
Difference between the pancreatic stimulatory effects of secretin and cholecystokinin: