Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

6. Describe how negative and positive feedback maintain body homeostasis.
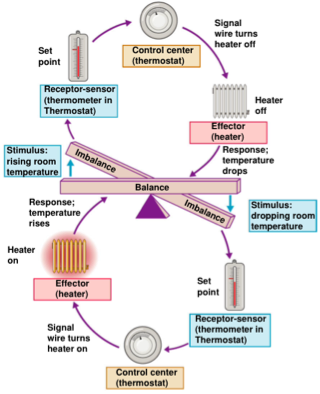
Negative Feedback
-In negative feedback systems, the output shuts off the original stimulus or reduces its intensity
-mechanisms cause the variable to change in a direction opposite to that of the initial change, returning it to its ideal value.
-Example: Regulation of room temperature via a thermostat connected to a furnace (e.g. hypothalamus in the body)
-Other mechanisms include blood volume, heart rate, blood pressure, respiration rate and depth, blood levels of O2 & CO2.
Positive Feedback
In positive feedback systems, the output enhances or exaggerates the original stimulus so that the activity (output) is accelerated.
The change that occurs proceeds in the same direction as the initial disturbance, causing the variable to deviate further and further from its original value.
Often referred to as cascades
Example: Labor contractions