Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

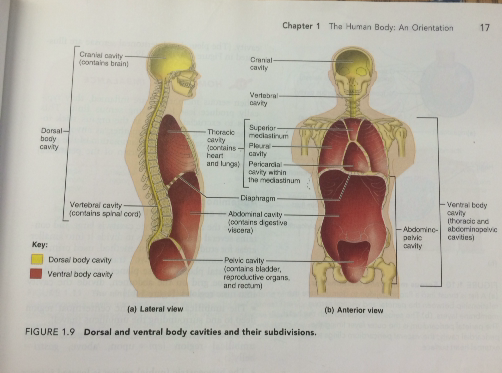
9) The Two Major Body Cavities and Their Subdivisions
The two major body cavities are the DORSAL BODY CAVITY and the VENTRAL BODY CAVITY. This cavities are closed to the outside and each contains internal organs.
The DORSAL BODY CAVITY- protects the fragile nervous system organs. The two subdivisions are the cranial cavity and the vertebral (spinal) cavity.
-The cranial cavity is located in the skull and encases the brain. The vertebral cavity runs within the bony vertebral column and encloses the spinal cord. The cranial and vertebral cavities are continuous with one another because the spinal cord is essentially a continuation of the brain.
The VENTRAL BODY CAVITY- is more anterior and a larger body cavity and collectively houses the visceral (internal) organs. This cavity also contains two subdivisons, the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.
-The thoracic cavity is surrounded by the ribs and muscles of the chest. The thoracic cavity is further subdivided into lateral pleural cavities which house both lungs and the medial mediastinum. The mediastinum contains the pericardial cavity which encloses the heart and surrounds the remaining thoracic organs (esophagus, trachea, etc.)
-The abdominopelvic cavity is a dome muscle that is important for breathing. The abdominopelvic cavity has two parts, the abdominal cavity and the pelvic cavity (these regions are not physically separated by a muscular or membrane wall. The abdominal cavity contains the stomach, intestines, spleen, liver and other organs. The pelvic cavity lies in the bony pelvis and contains the bladder, some reproductive organs and the rectum.