Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

35) Cutaneous, Mucous and Serious Membranes
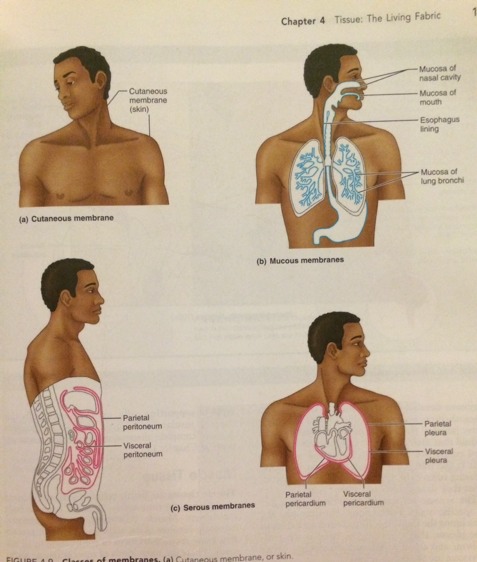
The Cutaneous Membrane- is the skin. It is an organ system consisting of a epidermis firmly attached to a think layer of dense irregular connective tissue (dermis). Unlike other epithelial membranes, the cutaneous membrane is exposed to the air and is a dry membrane.
The Mucous Membranes- line body cavities that open to the exterior such as hollow organs of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital tracts. Mucous membranes are moist membranes bathed by secretions. The term mucosa refers to the location of the membrane and not the cell composition, which varies. Most mucosae contain either stratified squamous or simple columnar epithelia. The epithelial sheet is directly underlain by a layer of loose connective tissue called the lamina propria. In some mucosae, the lamina propria rests on a third layer of smooth muscle cells. Mucous membranes are often adapted for absorption and secretion. The mucosae of both the digestive and respiratory tracts secrete copious amounts of lubricating mucus but the urinary tract does not.
The Serous Membranes- are the moist membranes found in closed ventral body cavaities. A serous membrane consists of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of loose connective (areolar) tissue. The mesothelial cells enrich the fluid that filters from the capillaries in the associated connective tissue with hyaluronic acid. The result is the thin clear serous fluid that lubricates the facing surfaces of parietal and visceral layers.