Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

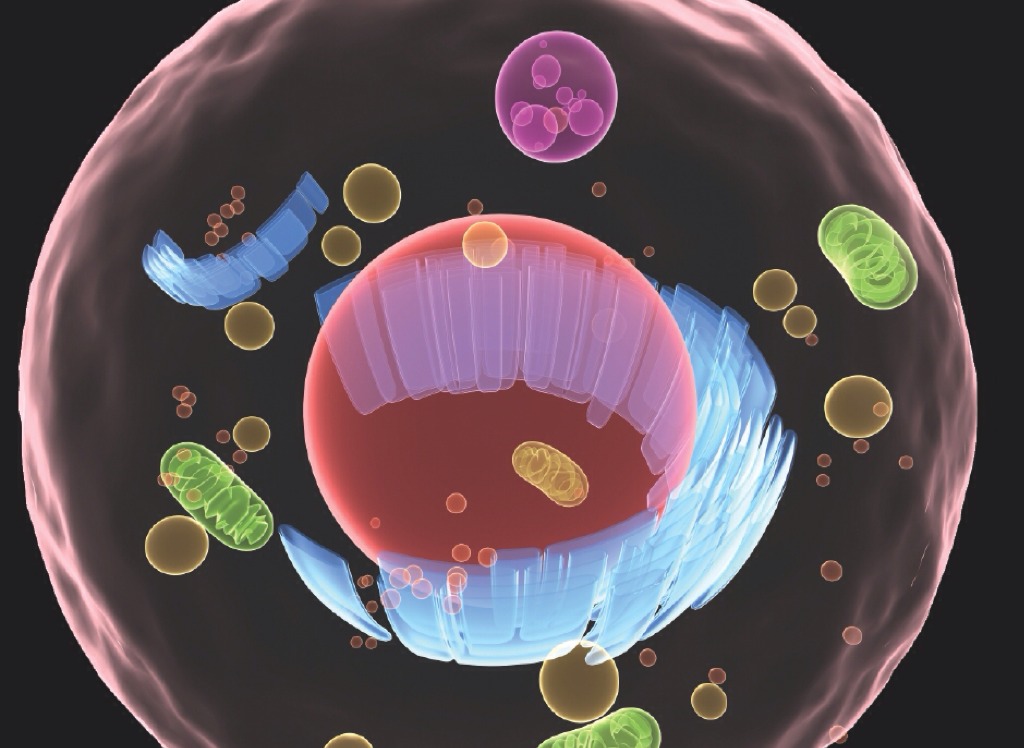
27. Ribosomes are small, dark-staining granules composed of proteins and a variety of RNA called ribosomal RNA. Each ribosome has two globular subunits that fit together and are sites of protein synthesis. Some float freely in the cytoplasm, while others are attached to membranes, forming a complex called the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosomes make soluble proteins that function in the cytosol. Membrane-bound ribosomes synthesize proteins destined either for incorporation into cell membranes or for export from the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an extensive system of interconnected tubes and parallel membranes enclosing fluid-filled cavities. It is continuous with the nuclear membrane and accounts for about half of the cell membranes. There are two versions of ER, rough ER and smooth ER. The external surface of the rough ER is studded with ribosomes. It's ribosomes manufacture all proteins secreted from cells. It is also the cells "membrane factory" because integral proteins and phospholipids that for part of all cellular membranes are manufactured there. The smooth ER is a continuation of the rough ER and consists of tubules arranged in a looping network. Its enzymes catalyze reactions involved with these processes: 1. Lipid metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and synthesis of the lipid components of lipoproteins, 2. Synthesis of steroid-based hormones such as sex hormones, 3. Absorption, synthesis, and transport of fats, 4. Detoxification of drugs, certain pesticides, and carcinogens, and 5. Breakdown of stored glycogen to form free glucose. The Golgi apparatus consists of stacked and flattened membranous sacs, shaped like hollow dinner plates, associated with swarms of tiny membranous vesicles. It is the "traffic director for cellular proteins. It has to modify, concentrate, and package the proteins and lipids made at the rough ER. The proteins are "tagged" for delivery to a specific address, sorted, and packaged in at least three types of vesicles that bud from the concave trans face of the Golgi stack. The Golgi apparatus also packages digestive enzymes into membranous lysosomes that remain in the cell.