Sign up for FlowVella
Sign up with FacebookAlready have an account? Sign in now
By registering you are agreeing to our
Terms of Service
Loading Flow

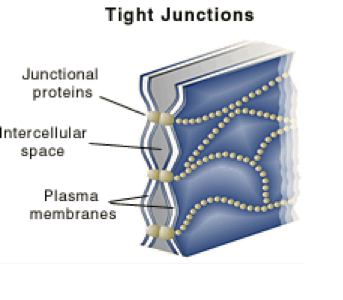
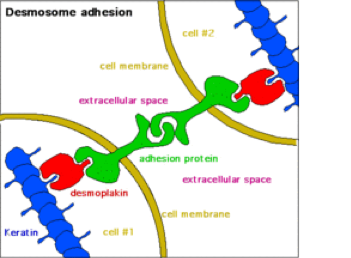
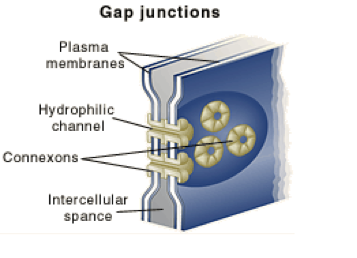
23. In a tight junction, a series of integral protein molecules in the plasma membranes of adjacent cells fuse together. They then form an impermeable junction that encircles the cell. Tight junctions help prevent molecules from passing through extracellular space between adjacent cells. Some tight junctions can be "leaky" and allow only certain types of ions to pass. Desmosomes are anchoring junctions-mechanical couplings scattered like rivets along the sides of abutting cells that prevent their separation. They not only bind neighboring cells together, they also contribute to a continuous internal network of strong "guy-wires." This distributes tension throughout a cellular sheet and reduces the chance of tearing when it is subjected to pulling forces. Desmosomes are abundant in tissues subjected to great mechanical stress, such as skin and heart muscle. A gap junction is a communicating junction that allows chemical substances to pass between adjacent cells. At gap junctions the adjacent plasma membranes are very close, and the cells are connected by hollow cylinders called connexons. These are composed of transmembrane proteins. Gap junctions are present in electrically excitable tissues, such as the heart and smooth muscle, where ion passage from cell to cell helps synchronize their electrical activity and contraction.